In today’s digital age, healthcare app development is revolutionizing the medical industry. These apps offer a range of services that improve patient care, streamline medical processes, and provide convenient access to health information. This article introduces the essentials of healthcare app development, covering the types of apps, key features, technologies, and benefits.
Healthcare App Development Process
Developing a professional healthcare app requires a thorough and structured approach to ensure it meets the needs of patients, healthcare providers, and administrative staff. The process involves multiple stages, from initial planning to deployment and maintenance. This article outlines the key steps involved in the healthcare app development process.
Idea Conceptualization and Market Research
Identifying the Need:
- Idea Generation: Define the purpose of the app and identify the target audience, whether it’s patients, doctors, or healthcare administrators.
- Market Research: Analyze market trends, user needs, and existing solutions. Identify gaps that your app can fill and understand the competitive landscape.
Defining Requirements and Planning
Setting the Foundation:
- Requirement Analysis: Gather detailed requirements from stakeholders, including the features and functionalities needed.
- Technical Feasibility: Assess the technical feasibility of the project, considering the technology stack and integration requirements.
- Project Planning: Develop a project plan with timelines, milestones, and resource allocation.
Designing the User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI)
Creating User-Friendly Designs:
- Wireframing: Create wireframes to map out the app’s layout and user flow.
- Prototyping: Develop interactive prototypes to visualize the user experience and gather feedback.
- UI Design: Design the app’s interface, focusing on aesthetics, usability, and accessibility. Ensure the design is intuitive and user-friendly.
Development
Building the App:
- Front-End Development: Develop the client side of the app, focusing on user interface and user experience.
- Back-End Development: Build the server side, including databases, server logic, and API integrations. Ensure secure data storage and processing.
- Integration: Integrate the app with necessary third-party services, such as EHR systems, payment gateways, and wearable devices.
Finding medical app developers is often tricky as such developers need to have domain and subject-matter knowledge about the healthcare sector and your niche in particular, which is not easy to come by. Hence, prefer working with a development agency that houses a team of app developers and subject-matter experts, as often both are separate profiles.
Testing and Quality Assurance (QA)
Ensuring Reliability and Performance:
- Functional Testing: Verify that all features work as intended and meet the requirements.
- Performance Testing: Assess the app’s performance under different conditions, including load testing and stress testing.
- Security Testing: Conduct security audits to ensure compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. Test for vulnerabilities and ensure data protection.
- Usability Testing: Evaluate the app’s usability with real users to gather feedback and make necessary improvements.
Deployment
Launching the App:
- App Store Submission: Prepare the app for submission to app stores (Google Play, Apple App Store). Follow the guidelines and ensure all requirements are met.
- Server Setup: Deploy the back-end infrastructure on reliable and scalable servers.
- Monitoring and Analytics: Set up monitoring tools and analytics to track app performance and user behavior post-launch.
Post-Launch Support and Maintenance
Continuous Improvement:
- User Support: Provide support to users through help desks, FAQs, and customer service channels.
- Regular Updates: Release regular updates to fix bugs, improve performance, and add new features.
- Feedback Integration: Continuously gather user feedback and integrate it into future updates to enhance the app’s functionality and user experience.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Ensuring Legal Adherence:
- Data Privacy: Ensure compliance with data privacy regulations such as HIPAA in the U.S. and GDPR in Europe.
- Certifications: Obtain necessary certifications and approvals for medical software, as required by local laws and regulations.
- Security Standards: Implement industry-standard security measures to protect sensitive health information.
The healthcare app development process involves a series of well-defined steps to ensure the app meets the high standards required in the medical field. From initial idea conceptualization to post-launch support, each stage is crucial in developing a successful healthcare app. By following a structured development process, healthcare app developers can create effective, secure, and user-friendly apps that significantly improve patient care and streamline healthcare services.
Types of Healthcare Apps
Healthcare mobile apps can be broadly categorized into three main types:
1. Patient Apps
- Telemedicine Apps: Enable virtual consultations with healthcare providers, allowing patients to receive medical advice and treatment remotely.
- Fitness and Wellness Apps: Track physical activity, diet, and overall health, helping users maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- Mental Health Apps: Provide resources and tools for managing mental health conditions, offering therapies and mindfulness exercises.
2. Doctor Apps
- Clinical Communication Apps: Facilitate secure communication between healthcare professionals for sharing patient information and collaboration.
- Diagnostic and Treatment Apps: Assist doctors in diagnosing conditions and recommending treatments based on medical data and algorithms.
3. Administrative Apps
- Electronic Health Record (EHR) Apps: Digitize patient records, making it easier to access and manage medical history.
- Appointment Scheduling Apps: Streamline the process of booking, rescheduling, and canceling appointments for both patients and healthcare providers.
Key Features of a Healthcare App
Healthcare apps are transforming the medical industry by providing easy access to health services and improving patient care. Effective healthcare mobile apps incorporate several essential features to enhance user experience and functionality. A well-designed healthcare app must include specific features to meet the needs of patients, healthcare providers, and administrative staff. Here are some of the salient features of a standard healthcare app MVP.
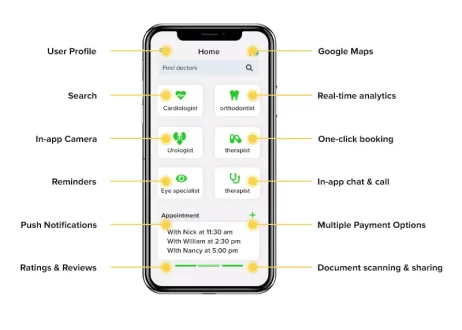
User Registration and Authentication
Secure Access:
- User Registration: Allows users to create accounts using email, phone number, or social media.
- Authentication: Secure login methods, such as two-factor authentication or biometrics, protect sensitive health information and ensure privacy.
Appointment Scheduling and Reminders
Convenient Booking:
- Appointment Booking: Users can book, reschedule, and cancel appointments directly through the app.
- Reminders: Automated notifications and reminders reduce no-shows and ensure patients do not miss their appointments.
Telehealth and Virtual Consultations
Remote Healthcare:
- Video Consultations: Real-time video calls with healthcare providers offer remote medical advice and treatment.
- Text and Voice Chat: Secure messaging options for follow-ups, prescription queries, and general advice enhance accessibility.
Electronic Health Records (EHR)/EMR Integration
Comprehensive Health Management:
- EHR Access: Integrates with existing EHR systems to provide seamless access to patient medical histories, test results, and treatment plans.
- Data Synchronization: Real-time synchronization ensures that all healthcare providers have up-to-date information.
Prescription Management
Efficient Medication Handling:
- e-Prescriptions: Doctors can prescribe medications electronically, reducing errors and enhancing efficiency.
- Prescription Reminders: Notifications remind patients to take their medications on time.
Health Monitoring and Tracking
Proactive Health Management:
- Wearable Integration: Connects with wearable devices to track vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and activity levels.
- Health Data Analytics: Analyzes collected data to provide insights and personalized health recommendations.
Secure Messaging and Communication
Confidential Communication:
- Real-Time Chat: Ensures secure communication between patients and healthcare providers.
- Multimedia Sharing: Allows the sharing of images, reports, and other multimedia files for better diagnosis and treatment.
Patient Education and Resources
Information Accessibility:
- Health Articles and Videos: Provides educational content about various health conditions, treatments, and wellness tips.
- FAQs and Help Sections: Offers answers to common queries and guides on using the app.
Payment Integration
Seamless Transactions:
- Multiple Payment Options: Supports various payment methods, including credit/debit cards, digital wallets, and insurance billing.
- Billing History: Allows users to view their payment history and download invoices.
Notifications and Alerts
Timely Updates:
- Appointment Reminders: Keeps users informed about upcoming appointments.
- Health Alerts: Sends notifications about important health updates, medication reminders, and test results.
Multi-Language Support
Inclusive Access:
- Language Options: Offers support for multiple languages, ensuring accessibility for a diverse user base.
User Feedback and Reviews
Continuous Improvement:
- Feedback Forms: Allows users to provide feedback on services and app performance.
- Ratings and Reviews: Helps other users make informed decisions and helps developers improve the app.
A successful healthcare app integrates essential features that cater to the diverse needs of patients, healthcare providers, and administrators. From secure user authentication to telehealth capabilities and EHR integration, each feature enhances the app’s functionality and user experience. By incorporating these salient features, healthcare apps can significantly improve patient care, streamline medical processes, and ensure better health outcomes.
Technologies Used in Healthcare App Development
Developing a robust healthcare app involves leveraging advanced technologies:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
- Enhance diagnostic accuracy, personalize treatment plans, and predict health outcomes based on data analysis.
2. Internet of Things (IoT)
- Connect wearable devices and sensors to collect real-time health data, enabling continuous monitoring and proactive care.
3. Blockchain
- Ensure secure and transparent health data management, enhancing data integrity and privacy.
4. Cloud Computing
- Provide scalable storage solutions and enable remote access to healthcare information, supporting telehealth services.
5. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
- Assist in medical training, remote surgeries, and patient education by creating immersive experiences.
Benefits of Healthcare Apps
Healthcare apps offer numerous benefits for patients, healthcare providers, and the healthcare system as a whole:
1. Improved Access to Care
- Make healthcare services more accessible, especially for patients in remote or underserved areas.
2. Enhanced Patient Engagement
- Empower patients to take an active role in managing their health through personalized insights and self-care tools.
3. Increased Efficiency
- Streamline administrative tasks and reduce the workload for healthcare providers, allowing them to focus more on patient care.
4. Better Health Outcomes
- Facilitate early detection and management of health conditions, leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
5. Data-Driven Decisions
- Enable healthcare providers to make informed decisions based on comprehensive and up-to-date patient data.
Design and User Experience in Healthcare Apps
Design and user experience (UX) play a critical role in the success of professional healthcare apps. These apps must be intuitive, accessible, and efficient to meet the diverse needs of patients, healthcare providers, and administrative staff. Let’s explore the essential elements of design and UX in healthcare mobile apps, highlighting best practices and key considerations.
Importance of UX in Healthcare Mobile Apps
Enhancing Patient Engagement:
- User-Centered Design: Focus on creating a user-centered design that prioritizes the needs and preferences of the users, making it easier for them to navigate and use the app.
- Accessibility: Ensure the app is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, by adhering to accessibility standards like WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines).
Key Elements of Healthcare App Design
Intuitive Interface:
- Simple Navigation: Design a simple and straightforward navigation system that allows users to find what they need quickly. Use clear labels, consistent icons, and logical flow.
- Minimalistic Design: Avoid clutter and keep the interface clean and minimalistic. Focus on essential features and information to prevent overwhelming the user.
Consistent Design Language:
- Consistency: Maintain a consistent design language throughout the app, including colors, fonts, and buttons. This helps users become familiar with the app and improves usability.
- Brand Identity: Reflect the brand’s identity in the design elements to create a cohesive and professional look.
User-Friendly Features
Personalization:
- User Profiles: Allow users to create profiles that store their personal health information, preferences, and history. This helps in providing personalized experiences and recommendations.
- Customized Alerts: Enable users to set preferences for notifications and alerts, such as appointment reminders and medication schedules.
Interactive Elements:
- Interactive Dashboards: Provide interactive dashboards that display health data in an easy-to-understand format. Use graphs, charts, and visual indicators to make data interpretation simple.
- Engagement Tools: Incorporate tools like goal setting, progress tracking, and feedback options to keep users engaged and motivated.
Best Practices for UX in Professional Healthcare Apps
Focus on Usability:
- Usability Testing: Conduct usability testing with real users to identify pain points and areas for improvement. Use feedback to refine the design and enhance user satisfaction.
- Onboarding Process: Design an effective onboarding process that guides new users through the app’s features and functions. Use tutorials, tips, and interactive guides to help users get started.
Prioritize Security and Privacy:
- Data Encryption: Ensure all health data is encrypted to protect user privacy. Use secure protocols for data transmission and storage.
- Compliance: Adhere to regulatory requirements such as HIPAA and GDPR to ensure the app meets legal standards for data protection and privacy.
Accessibility Considerations
Inclusive Design:
- Screen Reader Compatibility: Make sure the app is compatible with screen readers and other assistive technologies for visually impaired users.
- High Contrast Mode: Offer a high contrast mode to aid users with visual impairments. Ensure text is readable and interfaces are distinguishable.
- Voice Commands: Integrate voice command functionality to assist users who may have difficulty using touch controls.
Continuous Improvement
Iterative Design Process:
- User Feedback: Continuously gather feedback from users to identify areas for improvement. Implement changes based on user input to enhance the app’s usability and functionality.
- Regular Updates: Release regular updates to fix bugs, improve performance, and introduce new features. Keep users informed about updates and how they benefit them.
Design and user experience are crucial components of successful healthcare apps. By focusing on usability, accessibility, and continuous improvement, developers can create apps that effectively meet the needs of users while ensuring a positive and engaging experience. As these apps continue to evolve, prioritizing design and UX will remain essential in delivering high-quality digital health solutions.
Security and Compliance in Healthcare Apps
In the healthcare industry, security and compliance are paramount. Healthcare apps handle sensitive patient data, which requires stringent security measures and adherence to regulatory standards. So, let’s explore the critical aspects of security and compliance in such apps, highlighting best practices and key considerations.
Importance of Security in Healthcare Apps
Protecting Patient Data:
- Sensitive Information: Healthcare apps store and process sensitive data such as medical records, personal information, and financial details. Protecting this data from breaches and unauthorized access is crucial.
- Trust and Reliability: Ensuring robust security measures helps in building trust with users, which is essential for the app’s success and adoption.
Key Security Measures
Data Encryption:
- Encryption Standards: Implement advanced encryption standards (AES) to protect data at rest and in transit. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption key.
- End-to-End Encryption: Use end-to-end encryption for communications between patients and healthcare providers to ensure confidentiality.
Secure Authentication:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require MFA to add an extra layer of security, making it harder for unauthorized users to access the app.
- Biometric Authentication: Utilize biometric methods such as fingerprint and facial recognition for secure and convenient user authentication.
Access Controls:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implement RBAC to ensure that only authorized users have access to certain data and functionalities based on their roles.
- Audit Logs: Maintain detailed audit logs to track all access and actions taken within the app, which helps in detecting and responding to suspicious activities.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards
HIPAA Compliance:
- Protected Health Information (PHI): Ensure the app complies with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) by safeguarding PHI and following strict data handling protocols.
- Administrative Safeguards: Implement policies and procedures to manage the selection, development, and use of security measures to protect electronic PHI.
GDPR Compliance:
- Data Protection: Adhere to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to protect the personal data of users within the European Union.
- User Consent: Obtain explicit consent from users before collecting, processing, or sharing their data. Provide options for users to withdraw consent and delete their data.
Other Regional Regulations:
- Local Laws: Ensure compliance with other regional regulations such as CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) in the US, PIPEDA (Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act) in Canada, and similar laws in other jurisdictions.
- Cross-Border Data Transfers: Implement measures to comply with data transfer regulations when handling data across different countries.
Secure Development Practices
Security by Design:
- Threat Modeling: Conduct threat modeling during the development phase to identify and mitigate potential security risks.
- Secure Coding: Follow secure coding practices to prevent common vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and buffer overflows.
Regular Security Testing:
- Penetration Testing: Perform regular penetration testing to identify and address security weaknesses in the app.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Use automated tools to scan for vulnerabilities in the app’s code and infrastructure.
Data Privacy and User Control
Transparent Privacy Policies:
- Clear Communication: Provide clear and concise privacy policies that inform users about what data is collected, how it is used, and their rights regarding their data.
- User Control: Offer users control over their data, including options to access, modify, and delete their information.
Data Minimization:
- Essential Data: Collect and store only the data that is essential for the app’s functionality. This reduces the risk of data breaches and enhances user privacy.
Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
Real-Time Monitoring:
- Security Monitoring: Implement real-time monitoring tools to detect and respond to security threats promptly.
- Anomaly Detection: Use machine learning and AI to identify unusual patterns that may indicate a security breach.
Incident Response Plan:
- Preparedness: Develop and maintain an incident response plan to address security incidents swiftly and effectively.
- Notification Procedures: Establish procedures for notifying affected users and regulatory bodies in the event of a data breach.
Security and compliance are critical components of medical app development. By implementing robust security measures and adhering to regulatory standards, developers can protect sensitive patient data and build trust with users. Prioritizing security and compliance not only ensures the safety of healthcare information but also contributes to the app’s overall success and acceptance in the market.
Case Studies of Successful Healthcare Apps
Healthcare apps are transforming how patients interact with healthcare providers and manage their health. Several apps have set benchmarks for success by addressing specific needs and leveraging innovative technology. Let’s explore case studies of successful healthcare mobile apps that have made significant impacts on the healthcare industry.
MyFitnessPal
Overview:
MyFitnessPal is a comprehensive health and fitness app that helps users track their diet and exercise to achieve their fitness goals.
Key Features:
- Calorie Counter: A large database of foods with calorie and nutritional information.
- Exercise Tracker: Integration with various fitness devices and apps to log physical activities.
- Progress Tracking: Tools to monitor weight, calories, and nutrition over time.
Success Factors:
- User Engagement: MyFitnessPal’s interactive and user-friendly interface keeps users engaged and motivated.
- Community Support: A strong community feature allows users to connect, share progress, and offer support.
- Data Integration: Seamless integration with other health and fitness apps and devices enhances the user experience.
Impact:
- Health Outcomes: Many users report significant weight loss and improved health metrics.
- Market Presence: Over 200 million users worldwide, making it one of the most popular fitness apps.
Headspace
Overview:
Headspace is a meditation and mindfulness app designed to improve mental well-being through guided sessions and exercises.
Key Features:
- Guided Meditations: Sessions for stress, sleep, focus, and overall mental health.
- Sleep Stories: Narratives designed to help users fall asleep.
- Mindfulness Programs: Courses on mindfulness for different aspects of life, such as work and relationships.
Success Factors:
- User-Friendly Design: A clean, intuitive interface that makes it easy to find and follow meditation sessions.
- High-Quality Content: Professionally created content that appeals to both beginners and experienced meditators.
- Scientific Validation: Collaborations with researchers and clinical trials to validate the app’s effectiveness.
Impact:
- Mental Health: Users report reduced stress, better sleep, and improved focus.
- Recognition: Millions of downloads and high ratings on app stores, along with endorsements from mental health professionals.
Medisafe
Overview:
Medisafe is a medication management app that helps patients keep track of their medications and adhere to their prescribed treatment plans.
Key Features:
- Medication Reminders: Timely reminders to take medications.
- Drug Interaction Warnings: Alerts about potential interactions between different medications.
- Health Reports: Detailed reports on medication adherence and health outcomes.
Success Factors:
- Personalization: Customizable reminders and notifications tailored to individual medication schedules.
- Family and Caregiver Support: Options for caregivers to receive alerts and track a loved one’s medication adherence.
- Data Security: High standards for data privacy and security, ensuring user trust.
Impact:
- Adherence Rates: Significant improvement in medication adherence among users.
- Global Reach: Used by millions of people in over 150 countries.
Babylon Health
Overview:
Babylon Health is a telemedicine app that provides virtual consultations with doctors and AI-driven health assessments.
Key Features:
- Virtual Consultations: Video calls with certified doctors.
- Symptom Checker: AI-powered tool to assess symptoms and provide health advice.
- Health Monitoring: Tools to track health metrics and manage chronic conditions.
Success Factors:
- Accessibility: 24/7 access to healthcare professionals, reducing the need for in-person visits.
- AI Integration: Advanced AI algorithms to assist in preliminary diagnosis and health assessments.
- Comprehensive Care: Integration of telemedicine with in-app health tracking and management tools.
Impact:
- Patient Convenience: Reduced waiting times and increased access to healthcare, especially in remote areas.
- Health Outcomes: Early detection and management of conditions through continuous monitoring and AI assessments.
Practo
Overview:
Practo is an app that connects patients with healthcare providers, offering services like doctor appointments, telemedicine, and health records management.
Key Features:
- Doctor Search: Find and book appointments with doctors across various specialties.
- Telemedicine: Virtual consultations with healthcare providers.
- Health Records: Digital storage and management of health records.
Success Factors:
- Comprehensive Directory: Extensive database of healthcare providers, ensuring patients find the right doctor for their needs.
- Integrated Services: Combines appointment booking, telemedicine, and health records in one platform.
- User Trust: Strong reputation and user trust built over years of reliable service.
Impact:
- Accessibility: Easier access to healthcare services and specialists.
- Digital Health: Promotes the digital management of health records, improving continuity of care.
These case studies highlight the diverse ways healthcare apps can succeed by addressing specific needs, leveraging innovative technology, and focusing on user experience. From fitness tracking and mental health to medication management and telemedicine, these apps have set benchmarks in the industry, showing how digital solutions can significantly improve health outcomes and patient care.
Cost of Developing a Healthcare App
Developing a professional healthcare app involves a multifaceted process that requires careful planning, execution, and financial investment. The cost of creating such an app can vary widely depending on several factors, including the app’s complexity, features, design, and regulatory compliance requirements. Let us break down the main elements that influence the cost of healthcare app development and provide an overview of the potential expenses. The cost of healthcare app MVP development can be 20 to 50% of the total cost estimated here. Contact our team for a specific evaluation of your project.
Did you know? On ITProfiles.com, you can find the best healthcare app development companies to get quotes for your specific project.
Concept and Planning
Initial Costs:
- Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand the target audience, competitors, and market needs. This phase typically costs between $5,000 and $15,000.
- Requirement Analysis: Defining the app’s features, functionalities, and technical specifications. This can range from $2,000 to $5,000.
Design and User Experience (UX)
Design Expenses:
- Wireframing and Prototyping: Creating wireframes and interactive prototypes to visualize the app’s layout and user flow. This can cost between $5,000 and $10,000.
- UI/UX Design: Developing a user-friendly and visually appealing interface. The design phase can cost between $10,000 and $30,000, depending on the complexity and number of screens.
Development
Core Development Costs:
- Front-End Development: Building the client side of the app, including the user interface and user experience elements. This typically costs between $20,000 and $50,000.
- Back-End Development: Developing the server side, including databases, server logic, and API integrations. This can range from $25,000 to $60,000.
- Integration: Integrating third-party services such as Electronic Health Records (EHR), payment gateways, and wearable devices. Integration costs can vary from $10,000 to $30,000.
Testing and Quality Assurance (QA)
Testing Expenses:
- Functional Testing: Ensuring that all features work as intended. This can cost between $5,000 and $15,000.
- Performance Testing: Assessing the app’s performance under various conditions. This typically ranges from $5,000 to $10,000.
- Security Testing: Conducting security audits to ensure data protection and regulatory compliance. This can cost between $10,000 and $20,000.
- Usability Testing: Evaluating the app’s usability with real users. This usually costs between $5,000 and $15,000.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance Costs:
- HIPAA Compliance: Ensuring the app meets HIPAA regulations for handling Protected Health Information (PHI). Compliance measures can add $10,000 to $30,000 to the overall cost.
- GDPR Compliance: Adhering to GDPR regulations for data protection, especially if the app targets users in the European Union. GDPR compliance typically costs between $5,000 and $15,000.
- Other Regional Regulations: Ensuring compliance with other local laws and regulations, which can add $5,000 to $10,000.
Deployment
Deployment Expenses:
- App Store Submission: Preparing the app for submission to app stores (Google Play, Apple App Store), which can cost between $1,000 and $3,000.
- Server Setup: Setting up and configuring servers to host the app, which can range from $5,000 to $15,000.
- Monitoring and Analytics: Implementing tools to monitor app performance and gather user analytics, typically costing between $2,000 and $5,000.
Post-Launch Support and Maintenance
Ongoing Costs:
- Bug Fixes and Updates: Regularly update the app to fix bugs and add new features. This can cost between $10,000 and $30,000 per year.
- Customer Support: Providing ongoing support to users, which can range from $5,000 to $15,000 per year.
- Marketing and Promotion: Promoting the app to reach a wider audience, which can cost between $10,000 and $50,000 depending on the marketing strategy.
Total Cost Estimate
Overall Cost:
The total cost of developing a healthcare app can vary widely based on the scope and complexity of the project. On average, the total cost can range from $100,000 to $300,000 for a basic app with standard features. For more complex apps with advanced features and integrations, the cost can exceed $500,000.
The cost of developing a healthcare app is influenced by numerous factors, including design, development, testing, compliance, and ongoing maintenance. By understanding these elements, stakeholders can better plan their budget and ensure the successful development and deployment of the app. Investing in a high-quality, secure, and compliant healthcare app can lead to significant benefits, including improved patient care, streamlined medical processes, and enhanced user satisfaction.
Future Trends in Healthcare App Development
Healthcare app development is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and changing patient needs. As we look ahead, several trends are shaping the future of healthcare apps, promising to enhance patient care, improve efficiency, and make healthcare more accessible. Here we have covered some of the key future trends in medical app development.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Enhanced Diagnostics:
- AI Algorithms: Advanced AI algorithms are being developed to assist in diagnosing diseases more accurately and quickly. These algorithms can analyze medical images, patient histories, and genetic data to provide insights that aid in early detection and treatment planning.
- Predictive Analytics: Machine learning models can predict disease outbreaks and patient deterioration, allowing for proactive care and resource allocation.
Personalized Medicine:
- Tailored Treatment Plans: AI can analyze a patient’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and health data to create personalized treatment plans, improving outcomes and reducing side effects.
- Virtual Health Assistants: AI-powered virtual assistants can provide personalized health advice, medication reminders, and appointment scheduling, enhancing patient engagement and adherence to treatment.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
Expanding Access:
- Telehealth Services: The growth of telehealth services is making healthcare more accessible, especially for those in remote or underserved areas. Patients can consult with healthcare providers via video calls, reducing the need for in-person visits.
- Remote Monitoring: Wearable devices and IoT (Internet of Things) technology are enabling continuous monitoring of patient’s vital signs, allowing healthcare providers to track health metrics in real-time and intervene when necessary.
Improved Chronic Disease Management:
- Continuous Data Collection: Apps can collect data from wearable devices to monitor chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease. This continuous data collection helps in better disease management and timely interventions.
- Remote Patient Management: Remote monitoring tools allow healthcare providers to manage patients with chronic diseases more effectively, reducing hospital readmissions and improving quality of life.
Blockchain Technology
Enhanced Data Security:
- Immutable Records: Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent way to store health records. The immutability of blockchain ensures that patient data cannot be altered or tampered with, enhancing trust and security.
- Decentralized Data: By decentralizing data storage, blockchain reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, providing a more secure environment for sensitive health information.
Find top blockchain development companies for your project.
Interoperability:
- Data Sharing: Blockchain can facilitate seamless data sharing between different healthcare providers while ensuring patient consent and data privacy. This interoperability can improve care coordination and patient outcomes.
- Smart Contracts: Blockchain-based smart contracts can automate and streamline administrative processes such as insurance claims, reducing paperwork and processing times.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
Medical Training and Education:
- Immersive Learning: VR and AR technologies are being used to create immersive training environments for medical students and professionals. These tools provide realistic simulations of surgical procedures and clinical scenarios, enhancing learning and skill development.
- Patient Education: AR can be used to create interactive patient education tools, helping patients understand their conditions and treatment options better.
Therapeutic Applications:
- Pain Management: VR is being used as a tool for pain management, providing immersive experiences that distract patients from pain and anxiety during medical procedures.
- Rehabilitation: AR applications are helping in physical rehabilitation by providing real-time feedback and interactive exercises tailored to individual patient needs.
Voice Technology
Accessibility and Convenience:
- Voice Assistants: Voice-enabled healthcare apps are making it easier for patients to interact with their health information and manage their care. Voice assistants can help with tasks like medication reminders, appointment scheduling, and answering health-related questions.
- Hands-Free Operation: For healthcare providers, voice technology offers a hands-free way to access and update patient records, enhancing efficiency and reducing the risk of errors.
Integration with Smart Home Devices:
- Health Monitoring: Voice-activated devices integrated with smart home systems can monitor health metrics and provide alerts for abnormal readings, ensuring timely interventions and continuous care.
Genomic and Personalized Health Apps
Genetic Insights:
- Genomic Data Analysis: Healthcare apps are beginning to incorporate genomic data to provide personalized health insights and risk assessments. These apps can offer recommendations based on a patient’s genetic predispositions.
- Precision Medicine: By integrating genetic information, apps can help in creating more precise and effective treatment plans tailored to the individual’s genetic profile.
Holistic Health Management:
- Lifestyle and Environmental Factors: Future apps will consider a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors to provide comprehensive health management solutions.
- Preventive Care: Personalized health apps can promote preventive care by identifying potential health risks and suggesting lifestyle changes to mitigate them.
The future of healthcare app development is promising, with advancements in AI, telemedicine, blockchain, VR/AR, voice technology, and genomics driving significant improvements in patient care and health management. These trends are making healthcare more personalized, accessible, and secure, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and enhanced patient experiences. As technology continues to evolve, healthcare apps will play an increasingly vital role in the delivery of healthcare services.
Conclusion – Healthcare App Development
HealthTech is transforming the medical landscape by providing innovative solutions that enhance patient care and streamline healthcare processes. By incorporating advanced technologies and essential features, professional healthcare apps offer numerous benefits, making healthcare more accessible, efficient, and effective. As the industry continues to evolve, healthcare app development will play a crucial role in shaping the future of healthcare.
From the initial stages of concept and planning to the intricate process of design, development, testing, and deployment, developing a healthcare app involves numerous critical steps. Each phase demands careful consideration of user experience, regulatory compliance, and security to ensure the app meets the highest standards of functionality and safety.
Successful healthcare apps, as highlighted in our case studies, demonstrate the power of innovative solutions in enhancing patient engagement, improving health outcomes, and streamlining healthcare processes. Apps like MyFitnessPal, Headspace, Medisafe, Babylon Health, and Practo have set benchmarks by addressing specific needs and leveraging technology to provide exceptional services.
Looking to the future, trends such as artificial intelligence, telemedicine, blockchain technology, VR/AR, voice technology, and genomic integration are poised to drive the next wave of innovation in healthcare apps. These advancements will not only improve diagnostic accuracy and personalized treatment plans but also enhance accessibility, data security, and patient education.
Ultimately, the cost of developing a healthcare app is a worthwhile investment given the potential benefits. Whether through enhanced chronic disease management, seamless data sharing, immersive medical training, or voice-activated convenience, healthcare apps are reshaping the industry. By staying abreast of emerging trends and focusing on user-centric design and robust security measures, developers can create powerful tools that contribute to a healthier, more connected world.
Are you planning to develop your own healthcare app? Get advice from our experienced team building award-winning healthcare solutions and scaling successful startups and businesses for over 20 years. Contact us today for a free quote on your healthcare app development project.