Technology and healthcare have gone hand in hand for many years. Consistent forging ahead in the medical field has saved millions of lives and improved many others. As the year passes the healthcare industry is changing faster than ever before. With the broader availability of mobile internet, there is no telling what advances will come next. More than 80% of people these days prefer to use online services. Ever since right with a few clicks you can research conditions and the symptoms online. Just analyze, who wouldn’t like it if everything they want is available at their doorstep? Taking inspiration from this, Telemedicine came into the picture. We can say that Telemedicine has revolutionized the way the healthcare process is being done. Let’s learn in this article what is telemedicine and how does telemedicine work.
Telemedicine is a term that covers all of the ways you and your doctor can use technology to communicate without being in the same place. Telemedicine has a lot to offer when it comes to audio calls, video chats, emails, text messages, etc. The idea behind telemedicine is not to replace face-to-face consultation but to complement it. It is also known as Telehealth. Let us know what does telehealth mean.
What is Telehealth?
Telehealth care encompasses a broad range of healthcare services delivered through digital communication technologies. While often used interchangeably with telemedicine, telehealth is a more inclusive term that covers all aspects of remote healthcare, including both clinical services and non-clinical support. This includes telemedicine, but also extends to health education, administration, and wellness services.
What are the benefits of Telehealth?
Telehealth services revolutionize healthcare by significantly enhancing accessibility, convenience, and efficiency. By breaking down geographical barriers, it ensures patients, especially in remote or underserved areas, can access specialist care without the need for travel. Telehealth offers flexible scheduling and reduces costs for both patients and providers, while continuous monitoring and virtual check-ups improve the management of chronic conditions and overall health outcomes. During emergencies, like the COVID-19 pandemic, telehealth has proven vital in maintaining care while minimizing infection risks. Additionally, the integration of advanced technologies, such as AI and wearable devices, further optimizes patient care and engagement. As a scalable and equitable solution, telehealth promises a more sustainable and accessible future for global healthcare.
What is Telemedicine?
Telemedicine is revolutionizing healthcare by leveraging technology to provide medical services remotely. This innovative approach to healthcare has become increasingly important, especially in today’s fast-paced world where convenience and accessibility are crucial. In this article, we will explore what telemedicine is, its history and evolution, its importance, key features, how it works, who benefits from it, its impact on healthcare, and its future.
Telemedicine uses digital communication tools to provide clinical services to patients without an in-person visit. This includes video consultations, phone calls, and messaging services, allowing healthcare providers to diagnose, treat, and monitor patients remotely. It is particularly useful for patients with mobility issues, those living in rural areas, or anyone seeking more convenient healthcare options.
History and Evolution of Telemedicine
Telemedicine, the practice of providing medical care remotely using telecommunications technology, has a rich history that spans several decades. It has evolved significantly, particularly with advancements in technology, and has become an integral part of modern healthcare. Here’s a detailed look at the history and evolution of telemedicine:
Early Beginnings
1900s: The Inception
- Radio Communications: The concept of telemedicine can be traced back to the early 20th century when radio was used to provide medical advice to sailors on ships at sea. This marked the beginning of remote medical consultations.
1920s: First Attempts at Telemedicine
- Telegraph and Telephone: Doctors began using the telegraph and later the telephone to give medical advice. In the 1920s, a Dutch physician transmitted heart sounds over the telephone, one of the earliest documented cases of remote medical diagnostics.
Mid-20th Century Developments
1950s: Early Experiments
- Teleradiology: In the 1950s, one of the first instances of teleradiology was documented when radiologic images were sent via telephone lines between West Chester and Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
- Television Technology: The Nebraska Psychiatric Institute used closed-circuit television to provide psychiatric consultations to patients in Norfolk, Nebraska, over 100 miles away.
1960s: NASA and Telemedicine
- Space Program Innovations: The U.S. space program played a significant role in the development of telemedicine. NASA developed technology to monitor astronauts’ health remotely, which laid the groundwork for modern telemedicine practices.
Late 20th Century Expansion
1970s: Early Adoption
- Telemedicine Programs: Several early telemedicine programs were established. For example, in 1971, the Massachusetts General Hospital provided remote healthcare services to an airport medical station using a two-way television.
- Indian Health Service: The Indian Health Service implemented telemedicine to provide healthcare to Native Americans living in remote areas, demonstrating the practical applications of telemedicine in rural healthcare.
1980s: Technological Advances
- Computer Networks: The advent of computer networks facilitated the transmission of medical data. Hospitals began using computer networks to share medical records and consult specialists remotely.
- Videoconferencing: Advances in videoconferencing technology allowed for more interactive telemedicine consultations, improving the quality and effectiveness of remote care.
The Internet Era
1990s: Internet and Digital Technology
- Widespread Adoption: The proliferation of the internet in the 1990s revolutionized telemedicine. Email, online messaging, and video calls became commonplace in medical consultations.
- Telemedicine Organizations: Organizations such as the American Telemedicine Association (ATA) were founded to promote and support the use of telemedicine in healthcare.
21st Century: Mainstream Integration
2000s: Growth and Standardization
- Legislation and Reimbursement: Governments began to recognize the potential of telemedicine, leading to legislation that supported its use and reimbursement policies. The U.S. Medicare program, for instance, started reimbursing telemedicine services for rural patients.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): The adoption of EHRs facilitated the sharing of patient information among healthcare providers, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of telemedicine.
2010s: Technological Innovations
- Mobile Health (mHealth): The rise of smartphones and mobile apps led to the development of mHealth, where patients could use mobile devices to access healthcare services and track their health data.
- Telehealth Platforms: Specialized telehealth platforms emerged, offering a wide range of services, including virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and e-prescriptions.
The COVID-19 Pandemic and Beyond
2020s: Pandemic-Driven Surge
- Rapid Expansion: The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 dramatically accelerated the adoption of telemedicine. With lockdowns and social distancing measures in place, telemedicine became a vital tool for providing continuous healthcare.
- Policy Changes: Many countries temporarily relaxed regulations and expanded telemedicine services to cope with the increased demand. These changes included broader insurance coverage and more flexible guidelines for telemedicine practice.
Future Trends: Continued Evolution
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is expected to play a significant role in telemedicine, enhancing diagnostics, personalizing treatment plans, and improving patient outcomes.
- Remote Monitoring: Advances in wearable technology and remote monitoring devices will enable continuous health tracking and proactive medical interventions.
- Global Expansion: Telemedicine is poised to expand globally, reaching more underserved populations and integrating into various healthcare systems worldwide.
Importance of Telemedicine
- Accessibility: Telemedicine breaks down geographical barriers, providing access to medical care for those in remote or underserved areas.
- Convenience: Patients can receive care from the comfort of their homes, reducing the need for travel and waiting times.
- Continuity of Care: Telemedicine applications facilitate continuous monitoring and follow-ups, ensuring better management of chronic conditions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: It reduces healthcare costs by minimizing the need for physical infrastructure and lowering travel expenses for patients.
Key Features of Telemedicine
- Virtual Consultations: Video calls allow for face-to-face interaction between patients and healthcare providers.
- Remote Monitoring: Wearable devices and mobile apps track vital signs and health data, transmitting information to healthcare providers in real time.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Digital records ensure seamless sharing of patient information among healthcare providers.
- E-Prescriptions: Providers can prescribe medications electronically, which can be sent directly to pharmacies for convenience.
Who Benefits from Telemedicine
1. Patients
- Accessibility: Patients in remote or underserved areas can access medical care without the need for long-distance travel.
- Convenience: Patients can schedule and attend appointments from the comfort of their homes, reducing time off work and transportation costs.
- Reduced Waiting Times: Telemedicine often allows for quicker consultations, reducing the time patients spend waiting for appointments.
- Continuous Monitoring: Chronic disease patients can benefit from continuous remote monitoring and timely medical interventions.
2. Healthcare Providers
- Increased Reach: Providers can extend their services to patients in remote locations, broadening their patient base.
- Efficiency: Telemedicine can help healthcare providers manage their time more efficiently, scheduling more appointments and reducing no-shows.
- Work-Life Balance: The flexibility of telemedicine can improve work-life balance for healthcare professionals by reducing the need for travel between locations.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: Providers can maintain continuous communication with patients, leading to better health outcomes and patient satisfaction.
3. Rural Communities
- Access to Specialists: Rural residents can consult with specialists who are not available locally, receiving high-quality care without the need for travel.
- Improved Healthcare Delivery: Telemedicine can provide timely medical advice and intervention, crucial for areas with limited healthcare infrastructure.
4. Elderly and Disabled Individuals
- Mobility Challenges: Elderly and disabled individuals often face mobility issues that make travel difficult. Telemedicine allows them to receive care without leaving home.
- Home-Based Care: Telemedicine supports home-based care, enabling regular check-ins and monitoring without the need for in-person visits.
5. Chronic Disease Patients
- Ongoing Monitoring: Patients with chronic conditions, such as diabetes or hypertension, can be monitored continuously through telemedicine, enabling timely adjustments to treatment plans.
- Preventative Care: Regular virtual check-ups can help in the early detection and prevention of complications, improving overall health outcomes.
6. Mental Health Patients
- Access to Therapists: Telepsychiatry provides access to mental health professionals, which can be particularly beneficial for those in areas with a shortage of mental health services.
- Convenience and Privacy: Patients can attend therapy sessions from the privacy of their homes, which may reduce the stigma associated with seeking mental health care.
7. Parents and Caregivers
- Ease of Access: Parents can easily schedule virtual appointments for their children, managing their healthcare needs without disrupting their daily routines.
- Comprehensive Care: Telemedicine provides a convenient way to address various health concerns promptly, ensuring children receive timely medical attention.
8. Public Health Systems
- Resource Optimization: Telemedicine can help public health systems optimize resources by reducing the strain on physical healthcare facilities.
- Emergency Response: During public health emergencies, such as pandemics, telemedicine enables continued access to care while minimizing the risk of disease transmission.
Impact of Telemedicine on Healthcare
- Improving Access: It provides healthcare services to underserved populations and remote areas.
- Enhancing Efficiency: By reducing the need for in-person visits, telemedicine streamlines healthcare delivery and optimizes provider schedules.
- Increasing Patient Engagement: Patients are more likely to engage in their healthcare when it is easily accessible and convenient.
- Reducing Healthcare Costs: Lower overhead costs for providers and reduced travel expenses for patients contribute to overall cost savings.
The Future of Telemedicine
Over the past few years, the growing popularity of telemedicine is something that we all have been hearing about. But contrary to popular belief, telemedicine is not a concept that originated in the last decade. Telemedicine, as a concept, can be dated back to the 19th century. It originated due to the advent of telecommunication infrastructures such as the telegraph, telephone, and radio.
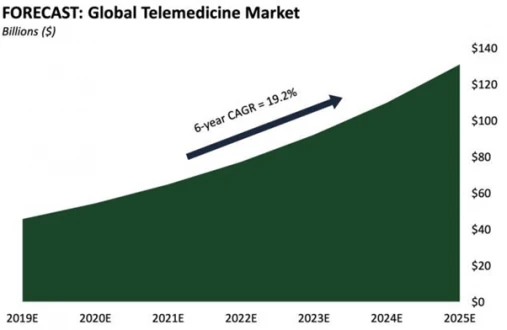
The earliest adoption of telemedicine technologies can be traced back to the Civil War when the use of a telegraph allowed casualties to be reported and even aided in ordering medical supplies. But today, telemedicine is an entirely different thing. As technology is advancing at an exponential rate, telemedicine is also changing faster than ever. But now let’s throw some light upon the most important lesson for any entrepreneur – how Telemedicine works.
How does Telemedicine Work?
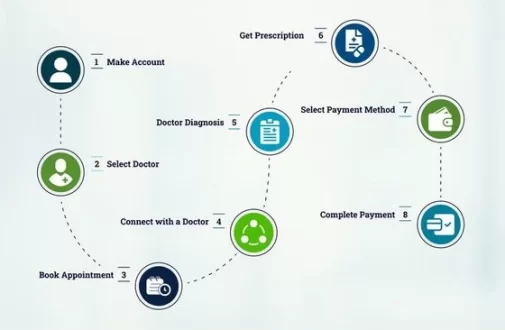
Telemedicine is described as the provision of remote clinical services, with two-way interaction between the patient and the doctor in real time. Such services can be especially beneficial during situations where the patient has a non-emergency medical problem that does not require the doctor to see the patient.
The most significant contribution of telemedicine to the healthcare industry is the convenience that it offers to both patients and medical practitioners. It allows patients to get medical advice while removing the necessity for a physical visit to the doctor. It not only saves time, but it is also cost-efficient. Furthermore, the ease of access and affordability of broadband internet services is taking telemedicine to the next level. Since video calls and audio calls are more feasible now, they are being incorporated into telemedicine technologies.
In late 2019, China successfully completed three remote surgeries, where doctors operated patients in remote physical locations with the help of surgical robots and a live feed of the operation. While this itself is beyond belief, what is more, unbelievable is that Dr. Hugo Gernsback predicted that sensory feedback devices would allow physicians to see their patients through a television screen and touch them from miles away with robot arms, in 1922, almost a century ago.
After reading all about Telemedicine and how does Telemedicine work, let us take a deep dive into how Teladoc works and who provides telemedicine services.
How does Teladoc Work?
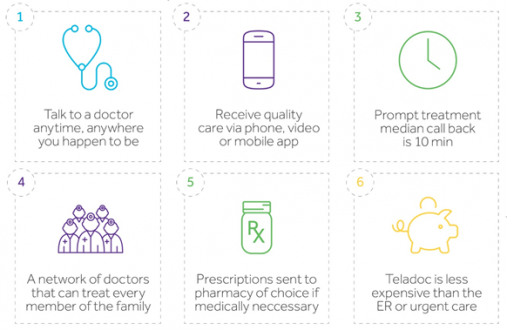
Teladoc is a virtual healthcare company in the United States that provides telemedicine services. Its comprehensive virtual care solutions are capable of serving organizations and patients all around the country. The company’s services are divided into the following six categories: platform and program services, guidance and support, expert medical services, mental health services, telemedicine, and integrated virtual care. The primary channels used by the company are telephone and video conferencing software. Teladoc’s on-demand remote medical care service allows patients to be connected to a board-certified, state-licensed physician within a few minutes, just by logging on to the service. The company earns money from individual consultations, but since its biggest customers are large employers and insurers, it generates most of its revenue through a yearly fee charged per subscriber. Taking inspiration from this Teladoc Clone proves to be one of the on-demand remote medical care solutions.
Start your own Telemedicine app
Are you planning to create your own telemedicine solution? Check out our complete guide on healthcare app development, which covers its process, types, features, costs, compliance, and more. And suppose you are looking for an end-to-end tech partner. In that case, you can get advice from our experienced team building award-winning healthcare solutions and scaling successful startups and businesses for over 20 years. Contact us today for a free quote on your food delivery app development project.

Your blogs are really helpful. Thanks for Sharing